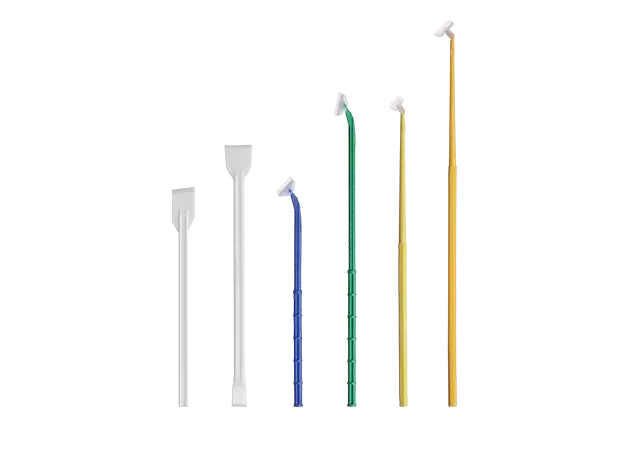Swab Tube Procurement Guide: How to Source Reliable and Compliant Products for Global Markets
In international medical supply trade, the swab tube is often treated as a low-value accessory. In reality, it is one of the most risk-sensitive components in any sampling or diagnostic workflow. A swab tube directly affects sample integrity, transport safety, regulatory acceptance, and customer trust. For overseas buyers sourcing swab tubes from Asia, problems rarely come from obvious defects. Instead, they come from small procurement oversights—unclear material standards, incomplete documentation, inconsistent dimensions, or packaging details that fail under international logistics conditions. At Kangjian, we work with global customers who source swab tube products for hospitals, laboratories, distributors, and diagnostic kit assembly. This guide is written from a practical procurement perspective, Kangjian explains how buyers can source reliable and compliant swab tube products for global markets with fewer surprises and fewer revisions.
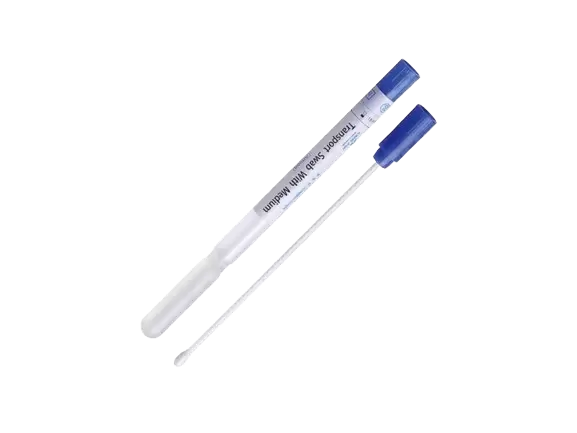

Clarifying Swab Tube Use Before Contacting Suppliers
Before asking for prices or samples, buyers should first define how the swab tube will actually be used. This step sounds simple, but it is where many sourcing mistakes begin.
Clinical and Diagnostic Sampling Use
In clinical scenarios, a swab tube is part of a controlled medical process. It must protect the sample from collection to analysis, often across long transport distances. In these cases, buyers should focus on whether the swab tube:
Maintains sealing integrity during transport
Is compatible with standard transport media
Uses materials that do not interfere with test results
For diagnostic use, even small variations in a swab tube—such as cap thread tolerance or internal volume—can cause workflow issues once the product enters real hospital or lab environments.
Laboratory and Research Applications
In research laboratories, swab tubes are often used repeatedly under controlled conditions. Buyers in this segment tend to care less about retail packaging and more about consistency and material stability.
A suitable swab tube for laboratory use should offer predictable dimensions, stable material performance, and reliable batch consistency. These factors matter more than visual appearance or branding.
Environmental and Food Safety Sampling
For environmental monitoring or food safety testing, a swab tube must perform reliably in non-clinical conditions. Temperature variation, rough handling, and extended storage are common. In these cases, buyers should prioritize durability, leakage resistance, and clear labeling to avoid sample confusion.
Swab Tube Specifications That Directly Affect Procurement Outcomes
When sourcing swab tubes internationally, technical details matter. Clear specifications help avoid misunderstandings between buyers and manufacturers.
Material Choice and Safety Performance
Most medical and laboratory swab tube products are made from polypropylene. This material is widely accepted because it offers good chemical resistance, stability, and compatibility with biological samples.
Buyers should always confirm that the swab tube uses medical-grade raw material, not general industrial plastic. This distinction often affects regulatory acceptance and long-term product stability.
Tube Size, Length, and Internal Volume
Swab tubes come in many sizes, and “standard” dimensions are not always universal. Buyers should verify that the swab tube:
Properly accommodates the full swab stick
Holds the required volume of transport media
Fits common storage racks and transport boxes
Incorrect sizing is one of the most common reasons buyers need to re-source after initial orders.
Cap Design and Leak Prevention
The cap is one of the most critical parts of a swab tube. During air or sea transport, pressure changes can expose weak sealing designs.
Buyers should pay attention to whether the swab tube uses a screw cap or snap cap, whether there is an internal sealing structure, and whether the supplier can provide leak test results. A well-designed swab tube should remain sealed from factory packing to final use.
Compliance and Documentation in Global Swab Tube Sourcing
Regulatory compliance is not optional in international markets. Even when a swab tube itself is simple, documentation requirements are often strict.
Medical Device Status Awareness
Depending on the market and application, a swab tube may be classified as a low-risk medical device. Buyers should understand how the product is positioned in their destination market and confirm that the supplier can support that classification.
Quality System and Certification Expectations
A reliable swab tube manufacturer should operate under recognized quality systems. Buyers typically request:
ISO 13485 for medical manufacturing
ISO 9001 for general quality control
Product conformity declarations
These documents help reduce delays during customs clearance and distributor registration.
Sterile and Non-Sterile Swab Tube Considerations
If a sterile swab tube is required, buyers must confirm sterilization methods, validation data, and shelf-life information. For non-sterile swab tubes, labeling clarity is just as important to avoid misuse in clinical settings.
Swab Tube Packaging and Labeling Details That Matter in Export Trade
Packaging quality often determines whether a swab tube arrives usable or compromised.
Primary Packaging Protection
Primary packaging must protect each swab tube from contamination, deformation, and moisture. For sterile swab tubes, packaging integrity directly affects usability.
Secondary Packaging for International Transport
For export orders, carton strength and pallet configuration matter. Weak secondary packaging can cause cap damage or tube deformation during transit, even if the swab tube itself is well designed.
Labeling Accuracy and Consistency
Clear labeling supports traceability and compliance. Buyers should ensure that each swab tube package includes product identification, batch information, manufacturer details, and sterility status where applicable.
Conclusion
Successful swab tube procurement depends on clear application definition, detailed specification review, regulatory alignment, and reliable supplier selection. By approaching swab tube sourcing as a regulated, performance-sensitive process, global buyers can avoid common pitfalls and build a stable supply chain.
At Kangjian, we support international customers with consistent, compliant swab tube solutions designed for real-world global trade requirements.